Difference Between a HEPA and ULPA Filter
Indoor air pollution carries dust mites, mold spores, and pollen causing health problems with individuals who have allergies or asthma. But, in a commercial environment such as an electronics manufacturing facility air pollution can damage electrical equipment being developed. High-efficiency air filters provide many benefits in maintaining a safe environment for personnel and prevent cross-contamination.
High-Efficiency Particulate Air (HEPA) and Ultra-Low Particulate Air (ULPA) filters are two of the most common air filters used in homes, automobiles, biomedical manufacturing, pharmaceutical manufacturing, semiconductor manufacturing, cleanrooms, and hospitals which require very clean air.
HEPA vs ULPA
Used in a commercial air filtration system, HEPA and ULPA share many similarities but differ in many aspects.
Similarities
Both HEPA and ULPA filters have been designed to trap very small particulate contaminants from an air stream by forcing air through a fine mesh. Typically composed of fiberglass randomly arranged forming a dense mat, fiber diameters are between .5 and 2 micrometers. A combination of three primary methods is used to trap particulates. Diffusion, interception and inertial impaction. And the final similarity between both filters, they will not remove gasses or odors. If you need to remove gases or orders from an environment an activated carbon filter may be ideal.
- Filter construction
- Filtration process
- Standard particulate filtration in critical environments
- Cannot remove gasses and odors
Pre-filtration can increase the life and performance of a filter.
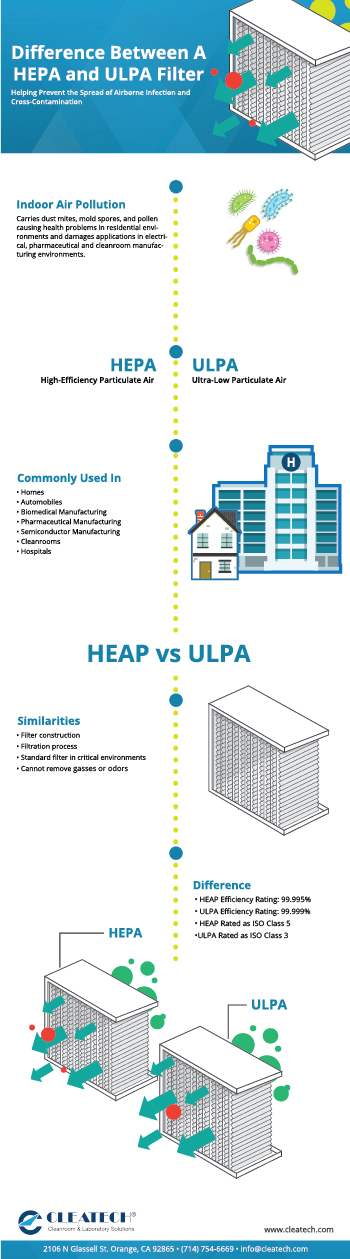
Difference
Now, let’s get into what is the difference between a HEPA and ULPA filter. As previously mentioned, both filters have been designed to remove very small particulate, but how efficient is each filter at removing the smallest of contaminants.
According to the United States Department of Energy (DOE), a HEPA filter should remove airborne particles 0.3 µm in diameter and ULPA filters should remove 0.1 µm in diameter. Rated at removing 99.999% of airborne contaminants, ULPA filters are considered more efficient than HEPA filters. A HEPA filters efficiency rating is 99.995%.
- HEPA efficiency rating: 99.995% removing airborne particles
- HEPA provide an ISO Class 5
- ULPA efficiency rating: 99.999% removing airborne particles
- ULPA provide an ISO Class 3
Filter Application
As we have learned, HEPA and ULPA filters are critical in preventing the spread of airborne allergens, infection, and cross-contamination in a range of commercial and residential environments. What else can HEPA/ULPA filters help protect? Common laboratory equipment used in the semiconductor, pharmaceutical, and biomedical industry require a filter to maintain a clean environment.
Here is a list of lab equipment that requires a HEPA or ULPA filters.
- Biosafety safety cabinets (BSC)
- Laminar flow hoods
- Containment glove boxes
- Closed-loop filtration glove box
- Ductless exhaust fume hoods

