Ducted vs. Ductless Fume Hoods
Ducted Fume Hood or Ductless Fume Hood? Before purchasing a fume hood there are a few variables to consider between a traditional chemical fume hood and a ductless fume hood.
A traditional fume hood is generally connected to a building HVAC System and relies on this system to remove hazardous fume from the laboratory. A ductless fume hood, as the name suggests, is a fume hood that does not depend on an exhaust system similar to an HVAC. Rather it filters fume through a set of filters attached to the unit. Let’s jump into the article and take a look at the pros and cons of each fume hood unit.
View available ducted and ductless fume hoods
Ducted Fume Hood
A Ducted Hood is attached to the buildings HVAC system. This allows contaminated air inside the laboratory to be pushed outside of the building and ensures the polluted air is not recirculated back into the laboratory. Figure 1 illustrates how this system functions.
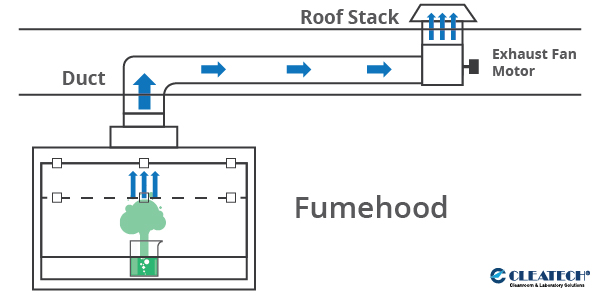
Ductless Fume Hood
As the name suggests, a ductless fume hood is not attached to a buildings HVAC system. Instead, a ductless hood moves contaminated air through HEPA (High-Efficiency Particulate Air) or ULPA (Ultra Low Particulate Air) filters and push the purified air back into the lab. Figure 2 illustrates how this system functions.
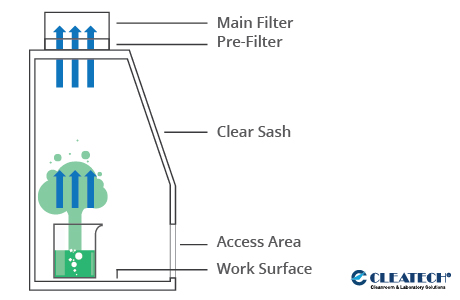
Pros & Cons
Ducted Fume Hood Pros
HVAC Exhaust System
An advantage a ducted fume hood has over a ductless hood is contaminated air being pulled by the building’s HVAC system and out of the building. This ensure hazardous particulate is not recirculated back into the workplace.
Broad Range of Chemicals
Since air is being filtered using the building’s HVAC system, this means a broader range of chemicals can be worked on inside the lab.
Ducted Fume Hood Cons
Attached to Buildings HVAC System
As mentioned above, having your fume hood attached to the buildings HVAC system is positive as it moves polluted air out of the building and replaced with purified air. Then why is this also on our cons list? The downside of being attached to the building’s HVAC system is if the system goes down or needs maintenance then your work is put on hold until the system is back online. Maintenance on an HVAC system is typically done twice a year, but if the system brakes then the downtime is unknown. This can cause a serious delay in your research.
Not a Portable Unit
Many labs will rearrange their layout to improve productivity. In most cases, a traditional ducted hood is connected to a stationary exhaust system. This stationary system will become difficult and costly when rearranging the lab layout.
Installation
A big factor in purchasing a ducted fume hood is making sure your laboratory has an existing fume exhaust system. Retrofitting a lab with this type of system can be extremely costly.
Ductless Fume Hood Pros
Installation and Cost
Installing a ductless fume hood is fairly easy. After the unit arrives and is unpacked, it’s a matter of moving the unit to the desired spot in the lab and plugging in the power cord. Most hoods are shipped as a turnkey solution. Since there is no cumbersome exhaust equipment to install around the lab, there is no additional cost.
Portable Unit
As you might have guessed, a ductless system allows for easy mobility. Not depending on an exhaust system, these units can be moved around the lab to an optimal location. The unit can be placed on a tabletop or a stand with casters can be purchased.
Ductless Fume Hood Cons
Limited Range of Chemicals
The chemical range is limited by the type of filter being used inside the fume hood. Depending on your application the filter may need to be swapped out to meet the purification needs. HEPA, ULPA, Activated Charcoal Carbon for General Purpose, and Activated Carbon for Acid Gasses filters are available.
Air Purification and Time Restraint
Unlike, a traditional fume hood, air is purified through filters at the top of the unit and pushed back into the laboratory, this has two drawbacks. A HEPA filter will capture up to 99.97% at 0.3µm particles, this leaves 0.03% particles recirculated back into the laboratory. If the application being worked on is releasing extremely dangerous fume working for a period of time can cause injury lab personnel.
Filter maintenance
Lab personnel may be required to replace the unit filters every year depending on the application and room condition. To avoid inhaling dangerous particles, the person changing the filter must wear protective gear at all times during this process. It will be the lab manager’s responsibility in assigning a lab technician when the time comes to change the hood filters.When considering to purchase a Ducted or Ductless Fume Hood, it is important to weigh the pros and cons to each unit. Each unit has its place in a lab, but it will depend on the lab’s budget, laboratory layout, and application. We hope this article helps you make an informed decision when purchasing your lab’s fume hood.
If you have any questions or need additional information, feel free to contact one of our specialists.

